Introduction
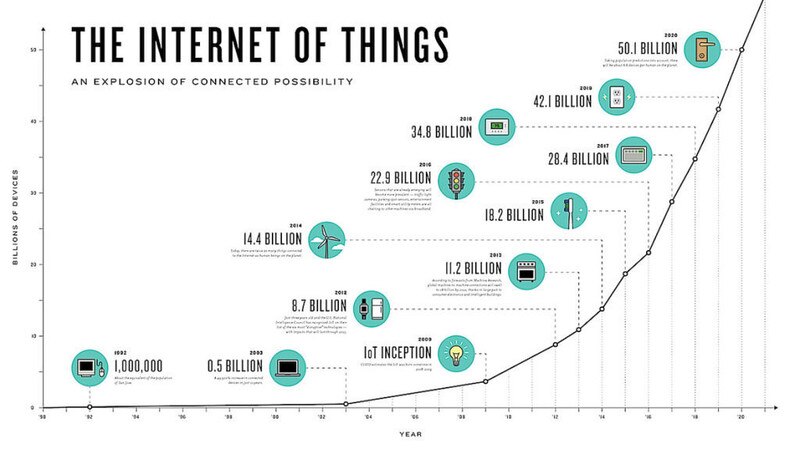
The Internet of Things (IoT) has quietly become the backbone of our digital civilization, with over 15 billion connected devices currently active worldwide. This invisible network of smart devices is transforming how we live, work, and interact with our environment. From smart homes to industrial automation, IoT technology is creating a seamlessly connected planet where data flows as freely as electricity.
A. The Explosive Growth of IoT
1. Current IoT Landscape
- 127 new devices connect every second
- Global market value reaching $1.1 trillion by 2025
- 83% of organizations report increased efficiency through IoT adoption
2. Key Growth Drivers
- 5G network expansion enabling massive device connectivity
- Plummeting sensor costs (now under $0.50 per unit)
- AI-powered analytics making IoT data actionable
- Energy-efficient chips extending device battery life
3. Demographic Adoption Trends
- 78% of US households own at least one smart device
- China leading in industrial IoT deployments
- European focus on privacy-centric IoT solutions
B. IoT’s Transformative Applications
1. Smart Cities Revolution
- Traffic Management: Adaptive signals reducing congestion by 30%
- Waste Optimization: Fill-level sensors cutting collection costs by 40%
- Public Safety: Gunshot detection systems with 90% accuracy
2. Healthcare Breakthroughs
- Remote patient monitoring reducing hospital readmissions by 50%
- Smart pills tracking medication adherence
- Emergency response systems with fall detection
3. Agricultural Innovations
- Soil sensors increasing crop yields by 25%
- Livestock monitoring improving herd health
- Automated irrigation saving 8 trillion gallons annually
C. The Technology Behind IoT
1. Connectivity Protocols
- LPWAN: For long-range, low-power applications
- Bluetooth Mesh: Creating dense device networks
- 5G NR: Enabling mission-critical IoT services
2. Edge Computing Evolution
- 45% of IoT data now processed at the edge
- Reduced latency from 100ms to under 5ms
- Enhanced privacy through local data processing
3. Power Innovations
- Energy harvesting from vibrations and RF signals
- Solid-state batteries lasting 10+ years
- Solar-powered sensors for remote deployments
D. Challenges in IoT Implementation
1. Security Vulnerabilities
- 57% of IoT devices vulnerable to medium-severity attacks
- Botnet attacks increasing 400% year-over-year
- Encryption gaps in legacy industrial systems
2. Privacy Concerns
- Location tracking without consent
- Voice data collection controversies
- Behavioral profiling through smart devices
3. Interoperability Issues
- 200+ competing IoT standards
- Cross-platform integration challenges
- Legacy system compatibility problems
E. The Future of IoT
1. Next-Generation Developments
- AIoT (AI + IoT) creating self-optimizing systems
- Digital twin technology for virtual replication
- Quantum IoT for unhackable communications
2. Market Projections
- 25 billion connected devices by 2027
- $1.6 trillion annual economic impact by 2030
- 79% of all internet traffic will be machine-to-machine
3. Societal Impacts
- Smart buildings reducing energy use by 35%
- Predictive maintenance saving $630 billion annually
- Personalized retail experiences boosting sales by 20%
Conclusion
The IoT revolution is just beginning to reveal its full potential as we progress toward a world where nearly every object can communicate, analyze, and act. While significant challenges around security and standardization remain, the benefits of this hyper-connected ecosystem are too profound to ignore. As IoT continues to mature, it will fundamentally reshape our relationship with technology, creating smarter, more responsive environments that anticipate our needs while optimizing global resource use.
Tags: IoT, smart devices, connected world, Internet of Things, IoT technology, smart cities, industrial IoT, IoT security, future technology, digital transformation
Category: Technology & Innovation