The quantum computing revolution has escalated into a high-stakes, billion-dollar arms race between nations and tech giants. As traditional computing approaches its physical limits, quantum systems promise to solve problems considered impossible for classical computers. This in-depth analysis explores the key players, technological breakthroughs, and potential economic impacts of this transformative technology that could redefine global power structures.
A. Understanding Quantum Computing Fundamentals
- Qubits vs Bits – Exploring superposition and entanglement principles
- Quantum Supremacy Milestones – Google’s 2019 breakthrough and beyond
- Major Quantum Approaches – Comparing gate-based, annealing, and topological methods
- Error Correction Challenges – The biggest hurdle in practical implementation
B. The Global Competition Landscape
- United States – IBM, Google, and startups backed by DARPA funding
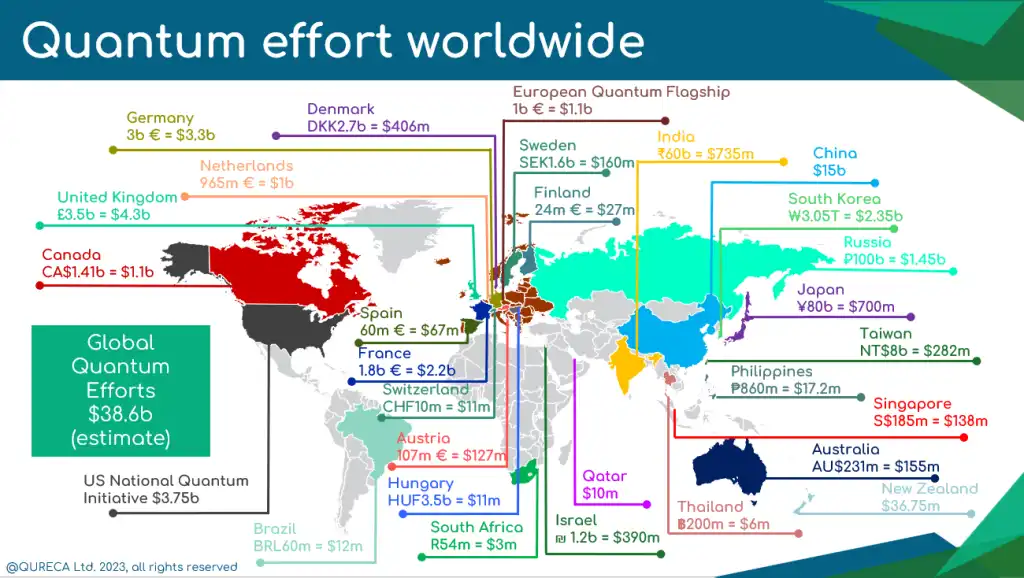
- China – $15 billion national quantum laboratory and satellite networks
- European Union – Quantum Flagship program’s €1 billion initiative
- Emerging Players – Canada, Australia, and Japan making strategic investments
C. Industry-Specific Quantum Applications
- Pharmaceuticals – Accelerating drug discovery through molecular modeling
- Finance – Quantum algorithms for portfolio optimization and fraud detection
- Climate Science – Modeling complex climate systems with unprecedented accuracy
- Cryptography – Breaking current encryption and developing quantum-safe alternatives
D. Tech Giants’ Quantum Strategies
- IBM’s Roadmap – 1,121-qubit Condor processor and quantum-centric supercomputing
- Google’s Approach – Focus on error correction and quantum AI applications
- Microsoft’s Unique Bet – Topological qubits and Azure Quantum ecosystem
- Amazon’s Play – Braket service democratizing quantum access
E. The Startup Ecosystem
- Rigetti Computing – Hybrid quantum-classical solutions
- IonQ – Trapped ion technology going public via SPAC
- PsiQuantum – Building fault-tolerant photonic quantum computers
- D-Wave – Commercial quantum annealing applications
F. National Security Implications
- Cryptographic Warfare – The looming threat to current security protocols
- Quantum Sensing – Ultra-precise navigation and submarine detection
- Military Applications – Pentagon’s advanced research projects
- Export Controls – Growing restrictions on quantum technology transfers
G. Investment Trends and Economic Potential
- VC Funding Surge – $1.4 billion invested in 2022 alone
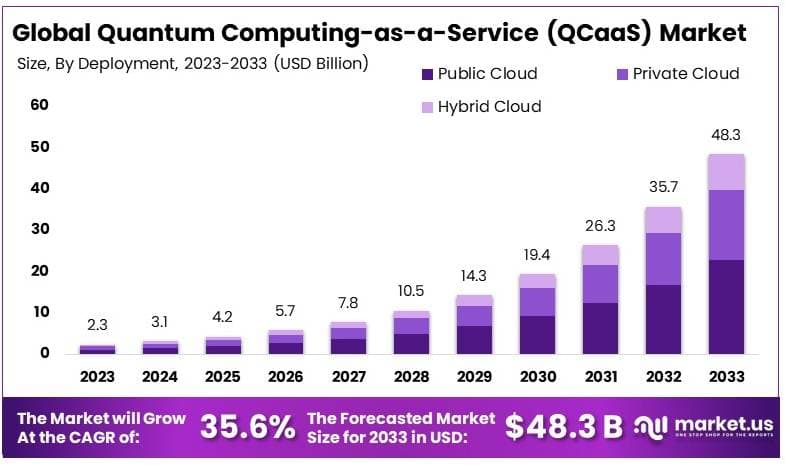
- Market Projections – $125 billion industry by 2030 forecasts
- Quantum Workforce – The scramble to educate next-gen specialists
- Patent Wars – Intellectual property battles heating up
H. Technical Challenges Remaining
- Qubit Stability – Maintaining coherence at scale
- Cooling Requirements – Extreme cryogenic environments needed
- Software Development – Creating quantum programming languages
- Integration Issues – Hybrid classical-quantum system architectures
I. Ethical Considerations and Risks
- Cryptographic Collapse – Preparing for post-quantum cybersecurity
- Economic Disruption – Industries that could be rendered obsolete
- Quantum Divide – Potential for new global technological inequality
- Dual-Use Dilemmas – Peaceful vs military applications
Conclusion
The quantum computing race represents one of the most significant technological competitions of our era, with the winners likely to gain substantial economic and strategic advantages. While full-scale, fault-tolerant quantum computers may still be years away, the current investments and breakthroughs are laying the groundwork for a quantum revolution that could transform every aspect of our digital lives. The nations and companies that can overcome the formidable technical challenges while addressing ethical concerns will shape the next epoch of computing history.
Tags: quantum computing, quantum technology, qubits, quantum supremacy, IBM quantum, Google quantum, quantum cryptography, quantum investment, future tech, quantum applications