The concept of the metaverse—a virtual, interconnected universe blending augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and the internet—has sparked global debate. As tech giants like Meta (formerly Facebook), Microsoft, and Google invest billions into its development, questions arise about its societal impact, economic potential, and ethical concerns. This in-depth guide explores the metaverse’s evolution, benefits, risks, and future implications.
A. What Is the Metaverse?
The metaverse is a collective virtual space where users interact through digital avatars, engage in immersive experiences, and even conduct business. Key components include:
-
Virtual Worlds – Persistent 3D environments (e.g., Decentraland, Roblox).
-
Augmented Reality (AR) – Overlays digital elements onto the physical world (e.g., Pokémon GO).
-
Virtual Reality (VR) – Fully immersive digital experiences (e.g., Oculus Rift).
-
Blockchain & NFTs – Enable digital ownership and decentralized economies.
-
Social Integration – Virtual meetings, concerts, and social hubs (e.g., Meta’s Horizon Worlds).
B. Why the Metaverse Matters
The metaverse is poised to transform multiple industries:
-
Digital Economy – Virtual real estate, NFTs, and crypto transactions create new revenue streams.
-
Remote Work – Immersive offices could replace traditional workspaces.
-
Education – Interactive VR classrooms enhance learning engagement.
-
Healthcare – VR therapy and AR-assisted surgeries improve patient outcomes.
-
Entertainment – Virtual concerts, gaming, and films redefine user experiences.
C. Key Players in the Metaverse Race
Several companies are leading the charge:
-
Meta (Facebook) – Investing $10B+ annually in VR/AR development.
-
Microsoft – Integrating Mesh for mixed-reality collaboration.
-
Google – Developing AR tools and cloud-based metaverse infrastructure.
-
Epic Games – Creator of Fortnite, expanding into virtual social spaces.
-
Decentraland – A blockchain-based virtual world powered by users.
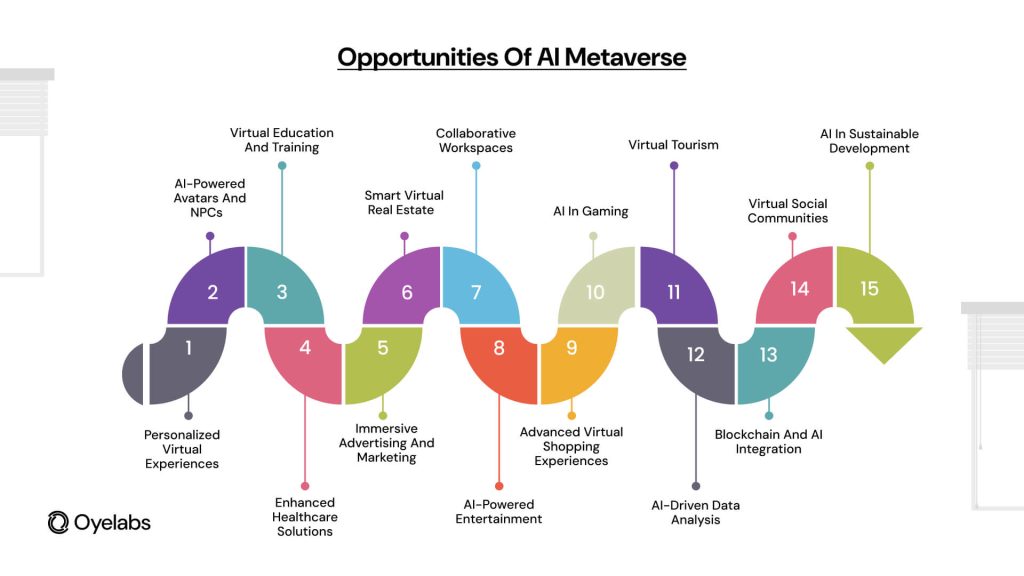
D. Opportunities in the Metaverse
-
Entrepreneurship – Sell virtual goods, offer services, or host events.
-
Marketing – Brands engage users via immersive ads and virtual stores.
-
Education – Universities offer VR courses for global accessibility.
-
Healthcare – VR exposure therapy for PTSD and phobias.
-
Social Impact – Virtual activism and global collaboration.
E. Ethical and Societal Concerns
-
Privacy Risks – Data collection in virtual spaces raises surveillance fears.
-
Addiction – Excessive immersion may harm mental health.
-
Digital Divide – Limited access exacerbates inequality.
-
Regulation Gaps – Lack of laws governing virtual crimes or fraud.
-
Identity Issues – Avatar anonymity could enable harassment.
F. The Future of the Metaverse
Experts predict:
-
Hybrid Reality – Seamless blending of physical and digital worlds by 2030.
-
AI Integration – Smarter NPCs (non-player characters) and personalized experiences.
-
Decentralization – Blockchain-powered metaverses reducing corporate control.
-
Healthcare Breakthroughs – VR-assisted surgeries and mental health treatments.
G. How to Prepare for the Metaverse Shift
-
Upskill Digitally – Learn VR/AR development or blockchain tech.
-
Invest Wisely – Research metaverse stocks, NFTs, or virtual real estate.
-
Stay Informed – Follow trends via tech news and industry reports.
-
Advocate for Ethics – Support policies ensuring inclusivity and privacy.
Conclusion
The metaverse represents both a revolutionary opportunity and a complex challenge. While it promises economic growth and innovation, ethical safeguards must keep pace with its development. Stakeholders—governments, corporations, and users—must collaborate to shape an inclusive, secure virtual future.
Tags: metaverse, virtual reality, augmented reality, blockchain, NFTs, digital economy, future tech, privacy concerns, VR gaming, remote work