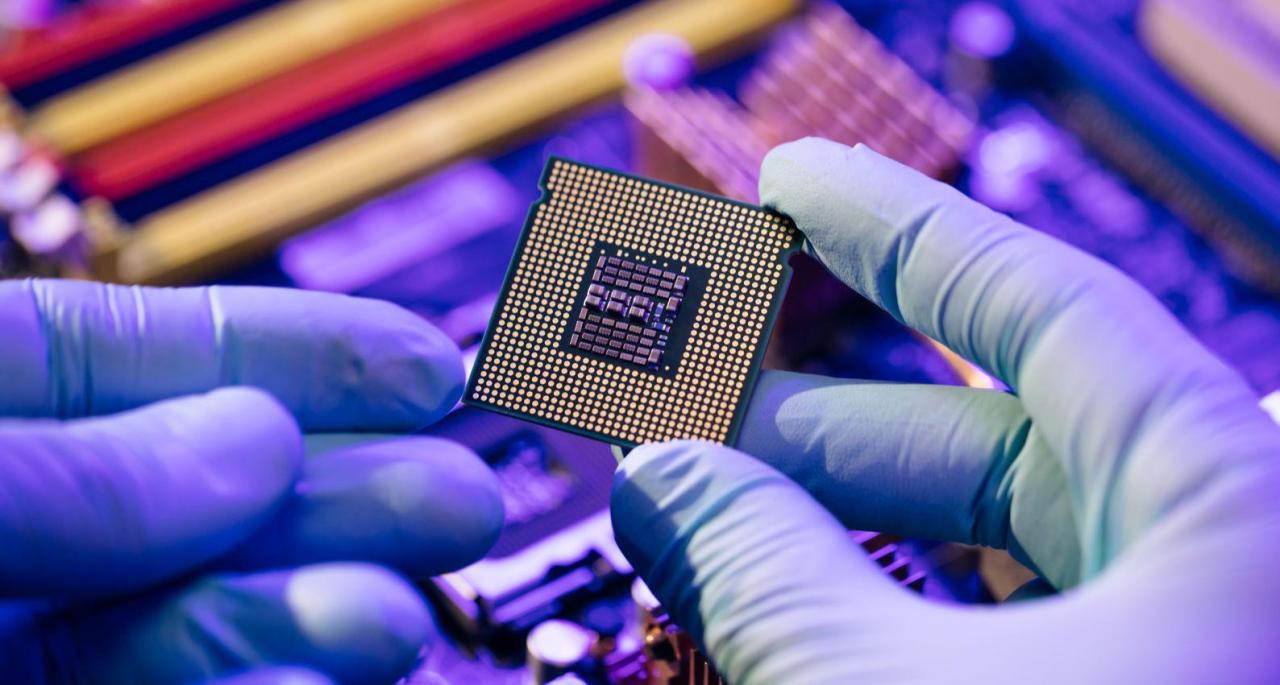
The world is facing an unprecedented semiconductor shortage, crippling production across major tech industries. From smartphones to automobiles, this crisis has forced companies like Apple, Tesla, and Samsung to delay product launches and slash production targets. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll examine the root causes of the chip shortage, its far-reaching consequences, and potential solutions to this global supply chain nightmare.
Why Semiconductors Are the New Oil
Modern technology runs on chips – these tiny silicon wafers power everything from:
-
Smartphones and laptops
-
Cloud computing infrastructure
-
Automotive electronics
-
Medical equipment
-
Home appliances
With demand skyrocketing and supply constrained, the tech world faces its most severe bottleneck in decades.
A. Root Causes of the Chip Shortage
A. Pandemic-Induced Demand Surge
-
Remote work requirements boosted PC and cloud server sales
-
Home entertainment needs increased gaming console demand
-
5G rollout accelerated smartphone upgrade cycles
B. Supply Chain Disruptions
-
COVID-19 factory shutdowns in Asia
-
Shipping container shortages
-
Geopolitical tensions affecting trade routes
C. Over-Reliance on Few Manufacturers
-
TSMC (Taiwan) and Samsung (Korea) dominate production
-
US and Europe account for just 12% of global chip manufacturing
D. Raw Material Shortages
-
Silicon wafers
-
Rare earth metals
-
Specialty gases
E. Unexpected Demand Spikes
-
Cryptocurrency mining boom
-
Automotive industry’s rapid electrification
B. Industries Hit Hardest by the Shortage
A. Consumer Electronics
-
Apple delayed iPhone production
-
PlayStation 5 remains chronically undersupplied
-
Laptop prices increased 20-30%
B. Automotive Sector
-
Ford cut 2022 production by 1.1 million vehicles
-
Tesla redesigned boards to use alternative chips
-
Used car prices hit record highs
C. Cloud Computing
-
Server costs rising for AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
-
Data center expansions delayed
D. Industrial Equipment
-
Factory automation systems backlogged
-
Medical device manufacturing slowed
C. Tech Giants’ Response Strategies
A. Vertical Integration Moves
-
Apple developing in-house modem chips
-
Tesla designing custom AI processors
B. Strategic Stockpiling
-
Samsung hoarding 3+ months of inventory
-
Cloud providers securing long-term contracts
C. Production Capacity Expansion
-
TSMC building $12B Arizona factory
-
Intel investing $20B in Ohio facilities
D. Product Redesigns
-
Using less advanced chips where possible
-
Software optimizations to reduce hardware demands
D. Long-Term Solutions Emerging
A. Geographic Diversification
-
CHIPS Act funding US semiconductor plants
-
European Chips Act aiming for 20% global share
B. Next-Gen Manufacturing
-
3nm and smaller process nodes
-
Chiplet architecture adoption
C. Alternative Materials Research
-
Gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors
-
Carbon nanotube experiments
D. Inventory Management Revolution
-
AI-powered demand forecasting
-
Just-in-case replacing just-in-time
E. When Will the Shortage End?
Industry analysts predict:
-
2023: Partial recovery for automotive sector
-
2024: Balance returning for consumer electronics
-
2025+: Full stabilization with new fabs operational
However, cyclical shortages may become the new normal as demand continues growing exponentially.
Conclusion
The global chip shortage represents both a crisis and opportunity for the tech industry. While current disruptions cause significant pain, they’re accelerating much-needed investments in semiconductor independence and next-generation technologies. Companies that adapt quickly will emerge stronger in the post-shortage landscape.