Introduction
The rollout of 5G technology is set to revolutionize urban living, enabling smarter, more efficient cities. With ultra-fast speeds, low latency, and massive connectivity, 5G will power innovations in transportation, energy management, public safety, and more. This article explores how 5G will shape the future of smart cities, the key benefits, challenges, and real-world applications.
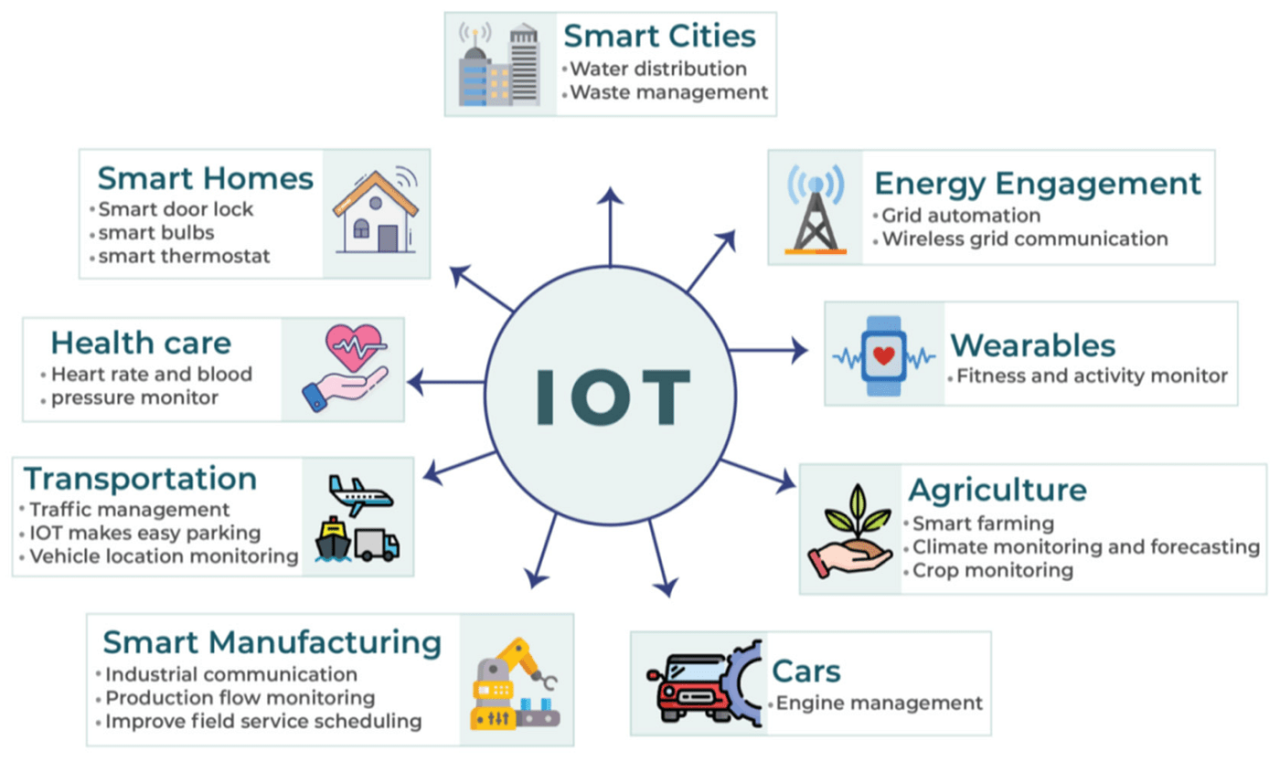
A. What Are Smart Cities?
Smart cities use digital technology to improve infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life. Key components include:
- IoT (Internet of Things): Sensors and devices collecting real-time data.
- AI & Big Data: Analyzing information for better decision-making.
- Connected Infrastructure: Smart traffic lights, energy grids, and waste systems.
5G acts as the backbone, enabling seamless communication between these systems.
B. How 5G Enhances Smart Cities
1. Faster and More Reliable Connectivity
- 5G offers speeds 100x faster than 4G, supporting real-time data processing.
- Low latency (1ms or less) ensures instant response for critical applications.
2. Improved Traffic and Transportation
- Smart Traffic Management: AI-powered signals reduce congestion by adjusting in real time.
- Autonomous Vehicles: 5G enables V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) communication for safer self-driving cars.
- Public Transit Optimization: Real-time tracking and predictive maintenance for buses and trains.
3. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Smart Grids: 5G helps balance energy demand, reducing waste and costs.
- Smart Streetlights: Adjust brightness based on activity, cutting electricity usage.
- Environmental Monitoring: Air quality sensors provide instant pollution data.
4. Enhanced Public Safety
- AI Surveillance: Facial recognition and anomaly detection for crime prevention.
- Emergency Response: Drones and connected ambulances reach incidents faster.
- Disaster Management: Early warning systems for floods, earthquakes, or fires.
5. Better Healthcare Services
- Telemedicine: Remote surgeries and real-time patient monitoring.
- Wearable Health Tech: Instant transmission of vital signs to doctors.
- Smart Hospitals: Automated systems for inventory and patient care.
6. Smarter Retail and Tourism
- AR Shopping: Virtual try-ons and interactive store navigation.
- Tourist Assistance: AI guides and real-time translation services.
C. Challenges in Implementing 5G for Smart Cities
1. Infrastructure Costs
- Installing 5G towers and fiber optics requires massive investment.
2. Security Risks
- Increased cyber threats targeting IoT devices and data networks.
3. Digital Divide
- Unequal access could widen the gap between high-tech and underserved areas.
4. Regulatory Hurdles
- Governments must establish policies for spectrum allocation and privacy.
D. Real-World Examples of 5G-Powered Smart Cities
1. Singapore
- Uses 5G for autonomous buses, smart lighting, and AI-based surveillance.
2. Barcelona
- Implements IoT sensors for waste management and water conservation.
3. Seoul, South Korea
- 5G-enabled holographic tourism guides and traffic control systems.
4. Dubai
- AI police officers and blockchain-powered government services.
E. The Future of 5G and Smart Cities
- 6G Research: Already underway for even faster, more integrated networks.
- AI & Edge Computing: Faster processing at the source (e.g., traffic cameras).
- Citizen Engagement: Apps allowing residents to report issues in real time.
Conclusion
5G is a game-changer for smart cities, enabling innovations that improve efficiency, safety, and sustainability. While challenges remain, the potential benefits make it a crucial investment for urban development. As technology evolves, cities worldwide will continue integrating 5G to create smarter, more livable environments.
Tags: 5G technology, smart cities, IoT, urban innovation, future tech, 5G benefits, smart infrastructure, AI in cities, sustainable cities, wireless connectivity
Category: Technology & Innovation