Introduction
Quantum computing represents one of the most revolutionary technological advancements of the 21st century. Unlike classical computers that use bits (0s and 1s), quantum computers leverage qubits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously through superposition and entanglement. This article explores the latest breakthroughs in quantum computing, their potential applications, challenges, and what the future holds for this transformative technology.
A. Understanding Quantum Computing Basics
1. Qubits vs. Classical Bits
- Classical Bits: Binary systems (0 or 1).
- Qubits: Can be 0, 1, or both simultaneously (superposition).
2. Key Quantum Principles
- Superposition: Qubits exist in multiple states at once.
- Entanglement: Linked qubits affect each other instantly, regardless of distance.
- Quantum Interference: Enhances correct computation paths while canceling errors.
3. Types of Quantum Computers
- Gate-Based Quantum Computers: Use quantum logic gates (e.g., IBM, Google).
- Quantum Annealers: Optimize solutions for specific problems (e.g., D-Wave).
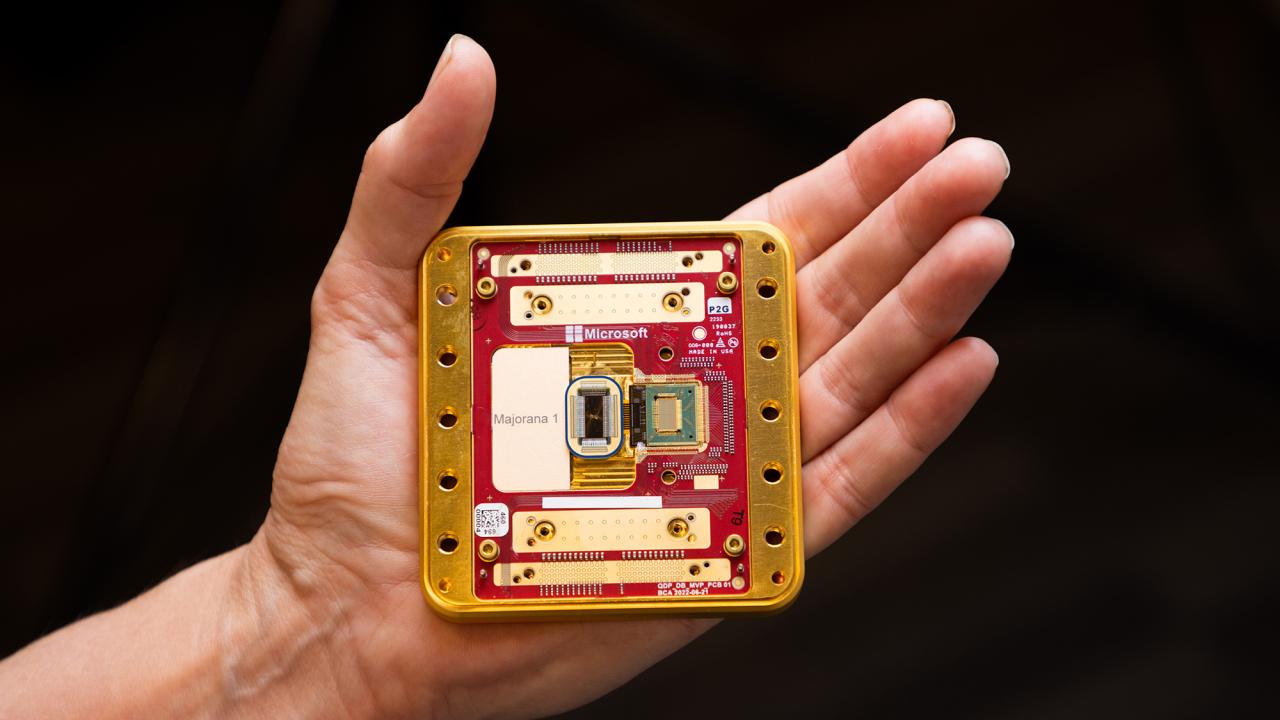
- Topological Quantum Computers: More stable qubits (Microsoft’s approach).
B. Recent Quantum Computing Breakthroughs
1. Quantum Supremacy Achievements
- Google’s Sycamore Processor (2019): Solved a problem in 200 seconds that would take a supercomputer 10,000 years.
- China’s Jiuzhang (2020): Demonstrated quantum advantage using photons.
2. Error Correction Improvements
- Surface Code Breakthroughs: Reduced qubit error rates significantly.
- Logical Qubits: Combining physical qubits to create more stable versions.
3. Longer Qubit Coherence Times
- IBM and MIT extended qubit stability from microseconds to milliseconds.
4. Scalability Advances
- Intel’s Horse Ridge II: Improved control of multiple qubits.
- Trapped-Ion Quantum Computers (IonQ): More scalable than superconducting qubits.
5. Hybrid Quantum-Classical Systems
- Companies like IBM and Amazon are integrating quantum processors with classical cloud systems for practical applications.
C. Potential Applications of Quantum Computing
1. Drug Discovery & Healthcare
- Simulating molecular interactions for faster drug development.
- Personalized medicine through genetic analysis.
2. Cryptography & Cybersecurity
- Breaking current encryption (RSA, ECC) with Shor’s algorithm.
- Quantum-resistant encryption development (e.g., lattice-based cryptography).
3. Financial Modeling
- Optimizing portfolios and risk analysis in real time.
- Fraud detection using quantum machine learning.
4. Climate Science & Energy
- Improving battery efficiency and fusion energy research.
- Carbon capture material simulations.
5. AI & Machine Learning
- Faster training of neural networks.
- Solving complex optimization problems.
6. Logistics & Supply Chain
- Route optimization for shipping and transportation.
- Inventory management using quantum algorithms.
D. Challenges Facing Quantum Computing
1. Qubit Stability & Decoherence
- Qubits lose their state quickly due to environmental interference.
2. Error Rates & Noise
- High error rates require advanced correction techniques.
3. Scalability Issues
- Current quantum computers have limited qubits (50-100).
4. Cooling Requirements
- Most quantum processors require near-absolute zero temperatures.
5. High Costs & Infrastructure
- Building and maintaining quantum systems is expensive.
E. Future of Quantum Computing
1. Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computers
- Expected by 2030, capable of running complex algorithms error-free.
2. Quantum Internet
- Secure communication networks using quantum entanglement.
3. Commercial Quantum Cloud Services
- Companies like IBM, Google, and AWS offering quantum-as-a-service (QaaS).
4. Industry-Specific Quantum Solutions
- Customized quantum applications for finance, healthcare, and logistics.
Conclusion
Quantum computing is poised to revolutionize industries by solving problems deemed impossible for classical computers. While significant challenges remain, ongoing breakthroughs in qubit stability, error correction, and scalability are accelerating progress. As research continues, quantum technology will unlock unprecedented possibilities in science, medicine, and beyond.
Tags: quantum computing, qubits, quantum supremacy, quantum applications, future tech, cryptography, AI, drug discovery, quantum challenges, quantum internet
Category: Technology & Innovation