Introduction
The digital landscape is facing an unprecedented surge in cybersecurity threats, with attacks growing in both frequency and sophistication. As organizations and individuals become increasingly reliant on digital systems, cybercriminals are exploiting vulnerabilities at an alarming rate. This comprehensive guide examines the current cybersecurity threat landscape, emerging attack vectors, protective measures, and future trends in digital security.
A. The Current State of Global Cybersecurity
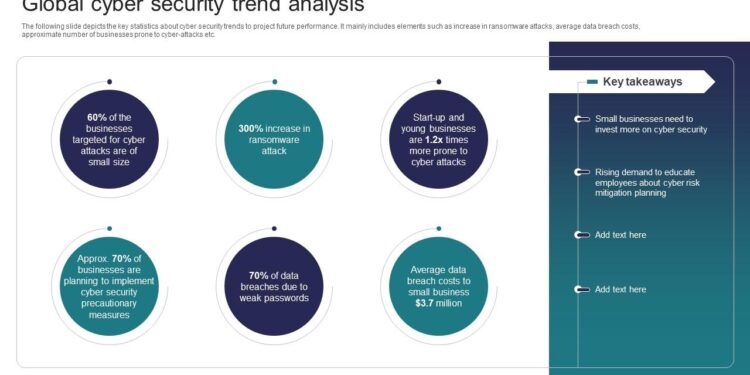
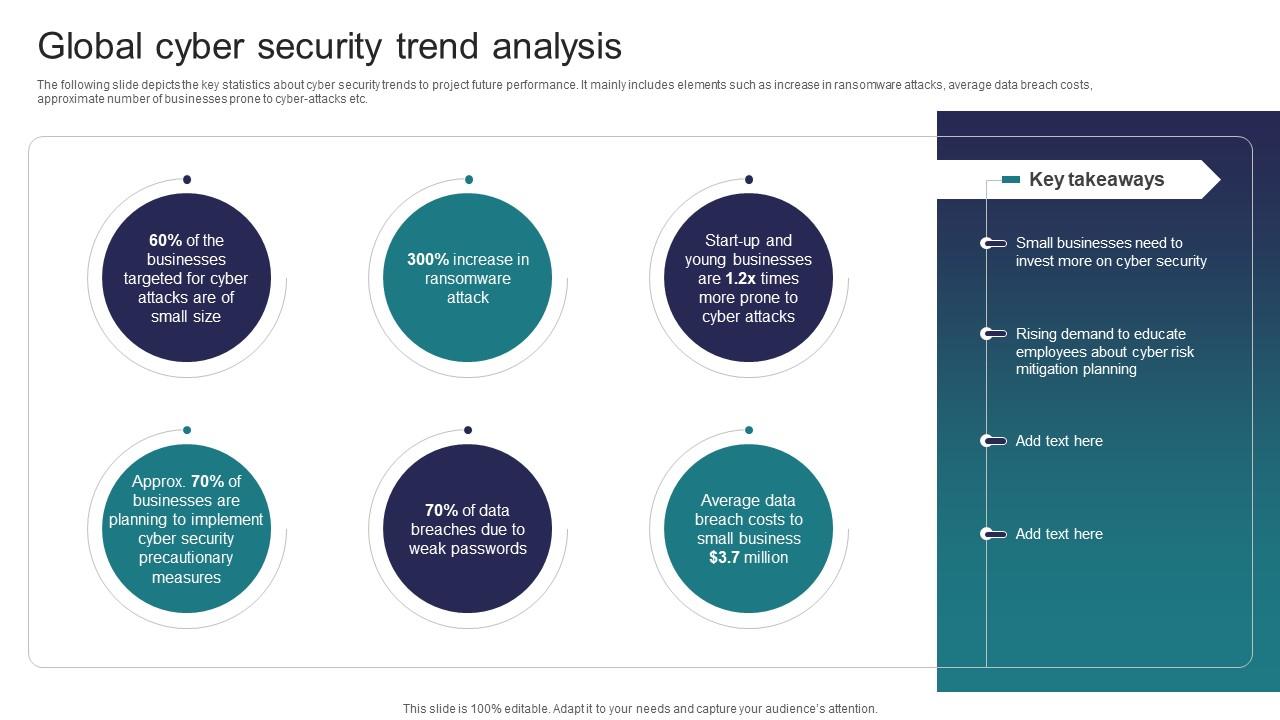
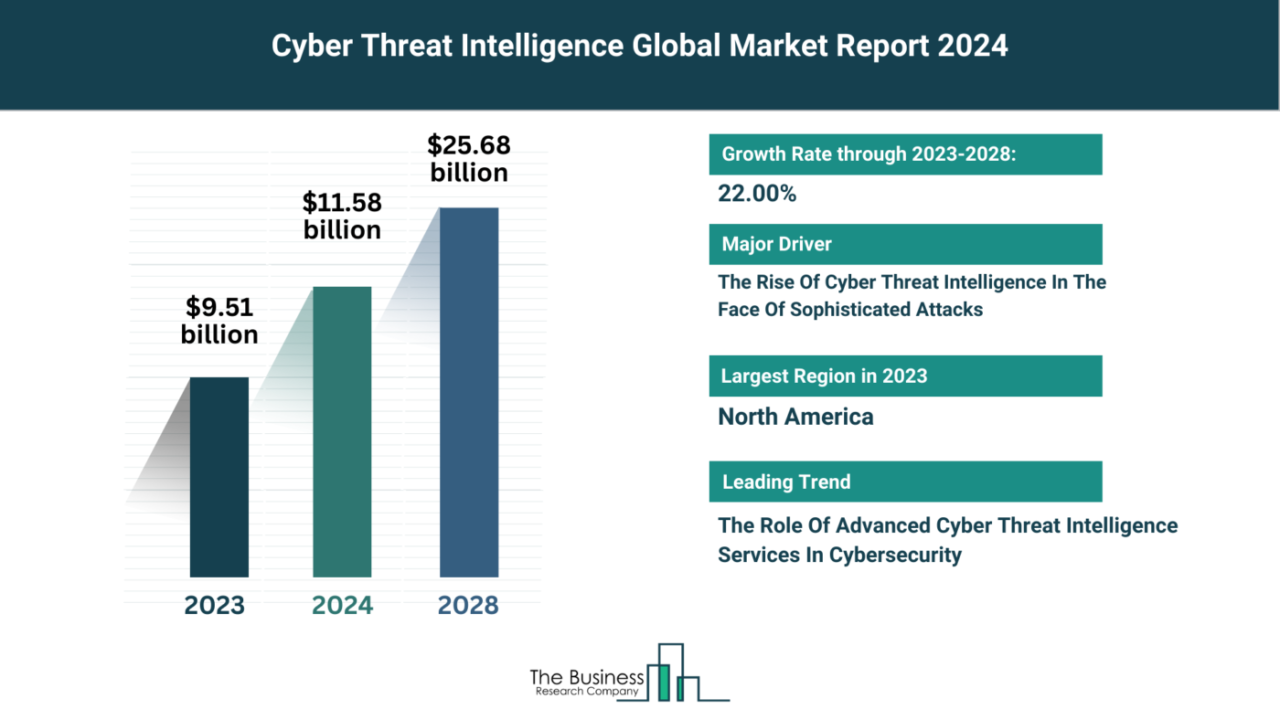
1. Statistical Overview of Cyber Threats
- 350% increase in ransomware attacks since 2018
- Average cost of data breach reaches $4.35 million (2022 figures)
- 80% of organizations report staff shortages in cybersecurity roles
2. Most Targeted Industries
- Healthcare (patient data theft)
- Financial services (banking fraud)
- Critical infrastructure (energy grids, transportation)
- Education (research data breaches)
3. Geographic Hotspots for Cybercrime
- North America (most targeted region)
- Asia-Pacific (fastest growing threat landscape)
- Eastern Europe (ransomware operations hub)
B. Emerging Cybersecurity Threat Vectors
1. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
- State-sponsored hacking groups
- Long-term infiltration strategies
- Examples: Lazarus Group, APT29
2. Ransomware Evolution
- Triple extortion tactics (data encryption + theft + DDoS)
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) marketplaces
- Critical infrastructure targeting
3. Cloud Security Vulnerabilities
- Misconfigured cloud storage
- API security gaps
- Containerization risks
4. AI-Powered Cyberattacks
- Machine learning for password cracking
- Deepfake social engineering
- Adaptive malware
5. Supply Chain Attacks
- Software dependency exploits
- Third-party vendor breaches
- SolarWinds-style compromises
C. High-Profile Cyberattack Case Studies
1. Colonial Pipeline Attack (2021)
- Ransomware shutdown of fuel infrastructure
- $4.4 million ransom paid
- National security implications
2. Log4j Vulnerability (2021)
- Ubiquitous software component flaw
- Estimated 100+ attempts per minute to exploit
- Ongoing remediation challenges
3. Twitter Celebrity Hack (2020)
- Social engineering attack
- Bitcoin scam netting $120,000
- Platform security overhaul
D. Cybersecurity Defense Strategies
1. Enterprise Protection Measures
- Zero Trust Architecture implementation
- Security Operations Center (SOC) optimization
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR) systems
2. Government Initiatives
- Critical infrastructure protection mandates
- International cybercrime cooperation
- Cybersecurity workforce development
3. Individual Protection Tips
- Password manager adoption
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Digital hygiene education
4. Emerging Defense Technologies
- Quantum cryptography
- Behavioral biometrics
- Deception technology
E. The Future of Cybersecurity Threats
1. Predicted Threat Landscape
- IoT device exploitation
- Space system vulnerabilities
- Quantum computing risks
2. Evolving Defense Paradigms
- Autonomous security systems
- Cyber insurance market growth
- Global cyber norms development
3. Workforce Challenges
- 3.5 million unfilled cybersecurity jobs
- Skills gap in cloud security
- Diversity in cybersecurity recruitment
Conclusion
The global surge in cybersecurity threats represents one of the most significant challenges of our digital age. As attack methods grow more sophisticated, a multi-layered defense approach combining technological solutions, policy measures, and user education becomes increasingly critical. Organizations must prioritize cybersecurity investments, while individuals should remain vigilant about digital security practices. The evolving threat landscape demands continuous adaptation and international cooperation to protect our interconnected digital ecosystem.
Tags: cybersecurity, cyber threats, ransomware, data protection, cyber attacks, digital security, online safety, hacking prevention, information security, cyber defense
Category: Technology & Digital Security